
Hafiz Khalid, XP Power's Director of Product Marketing, discusses why achieving both the precision and accuracy needed in high voltage DC power supplies can be tricky for designers and how to overcome this challenge.
Overview
- Both precision and accuracy are needed in power supplies for high voltage applications.
- Careful component selection and adherence to safety standards are essential to achieve high precision.
- A pre-certified, bought-in power supply is often a cost-effective solution with minimum design risk.
Many people use the terms ‘accuracy’ and ‘precision’ interchangeably. However, these terms have separate and different meanings which must be used carefully when evaluating the performance of high voltage power supplies.
Accuracy and precision – what's the difference?
'Accuracy' can be described as how closely a quantity or action resembles the true or accepted value, while 'precision' can be described as how closely related two consecutive actions are.
Look at the image below. The shots grouped evenly around, but away from the target center, are accurate but not precise. Shots which are all off-center, but closely grouped together, are precise but not accurate.
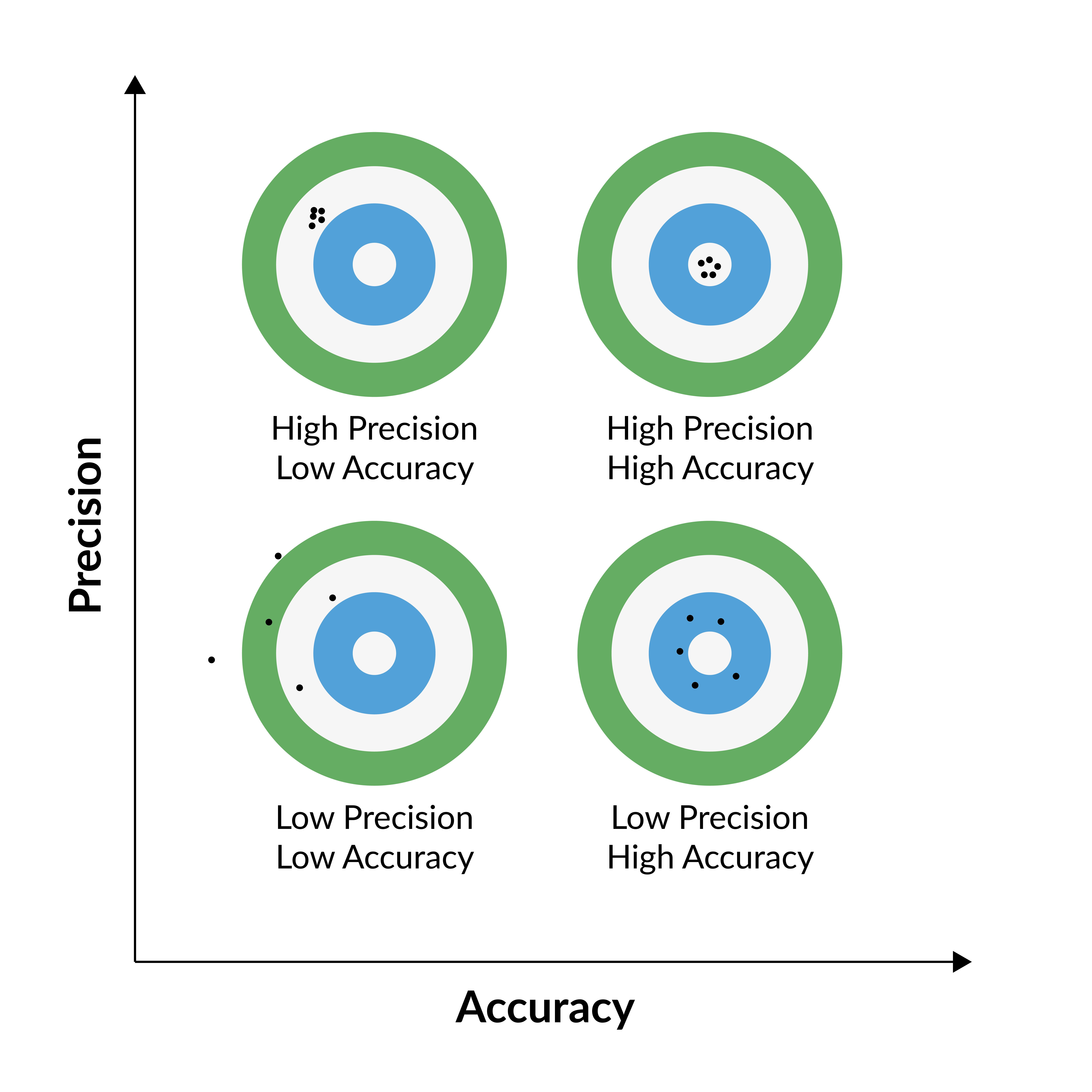
For a high voltage power rail, any of the combinations in the above image could be acceptable – depending on the application of course. Electrostatic chucks need relatively low accuracy but high precision (for consistency) from a high voltage power supply, for example.
When do you need both high accuracy and precision?
Some applications require precise and accurate power supplies to maintain stable outputs over load and line changes, multiple units, time, and changing environmental conditions. Examples include powering sensitive equipment like photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) used in scanning electron microscopes, mass spectrometers, and medical imaging.
The accuracy and consistency of measurements, as well as long-term stability and repeatability, are crucial in these applications. High voltage supplies are often used in highly sensitive operations such as e-beam lithography in semiconductor manufacturing and piezoelectric drives for lens/mirror positioning.
Contrasting general purpose power supplies with high voltage power supply specifications
General purpose power supplies have typical specifications that are widely accepted, with an initial voltage accuracy of +/-2%, regulation of 0.5% from 10% load to full output, and 1% maximum ripple and noise in a 20MHz bandwidth.
However, for high voltage applications like e-beam microscopy or e-beam lithography, much higher levels of precision are required, with line and load regulation of 0.02% - 0.0001% and peak-to-peak ripple and noise of 0.0005%/5ppm of rated voltage.
How to achieve high precision in your power supply
Achieving the desired level of precision in a power supply requires careful design decisions using precision temperature-compensated voltage references, laboratory-quality resistors, and low-noise conversion topologies. The internal converter transformer design and careful placement of screens are also crucial for low noise and high isolation. Modular converters are often enclosed in metallic enclosures for screening and safety isolation.
Tips for making the right high voltage power supply design choices
You want your power supply to be as long-lasting, reliable and compact as possible. Careful design topology selection and transformer design will ensure your supply is accurate and precise, but you should also bear the tips in mind:
- Minimize dissipation through high sensing impedances.
- Protect outputs and prevent arcing through carefully controlled leakage current and/or encapsulation.
- Comply with safety standards by scaling creepage and clearance distances.
- Avoid points of high electric field intensity and consequent breakdown by routing PCB tracking without sharp corners.
- Achieve better dielectric strength by choosing materials such as high voltage TeflonTM.
- The benefits of a pre-certified, bought-in power supply.
Achieving both the precision and accuracy needed in high voltage DC power supplies can be tricky for designers. One way to overcome this challenge is by selecting a bought-in, pre-certified product such as XP Power’s HCP or CA series. This is often the most cost-effective solution, involving minimum design risk and helping you get your product to market quickly.
Please feel free to contact us for more information regarding our precision solutions for your high voltage challenges.








